Sodium Hexametaphosphate: Exploring the Uses and Characteristics of the Product
Definition and Chemical Structure
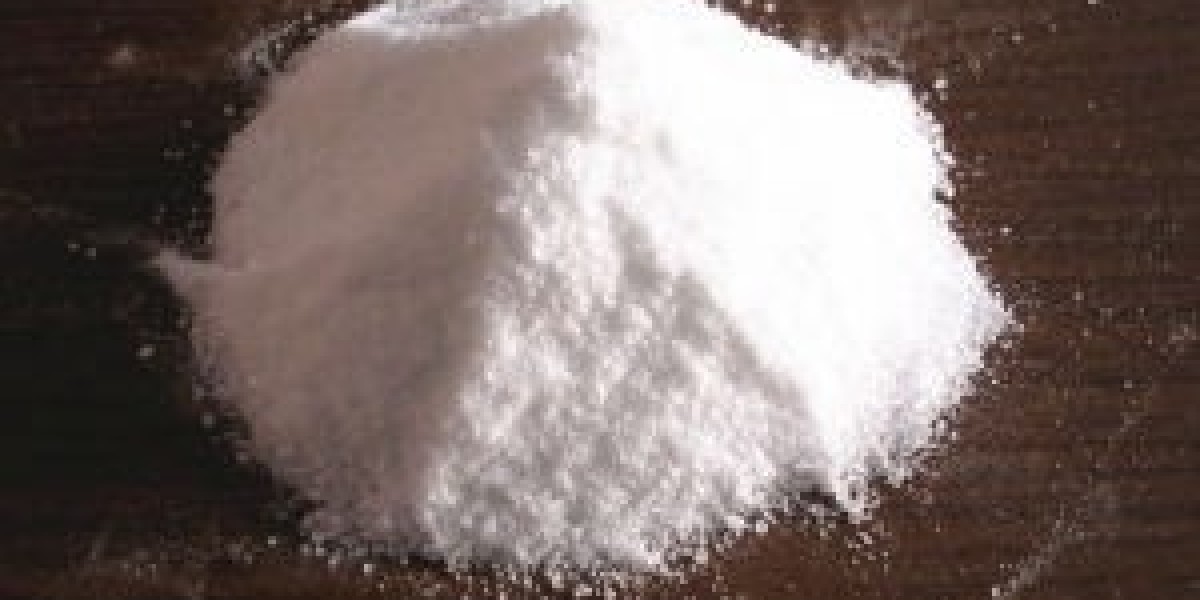
Sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NaPO3)6. It is a type of polyphosphate composed of alternating (PO3)n chains that are joined together at the phosphate ends, forming a ring structure. In the formula, six (PO3) units are bonded together through shared oxygen atoms to give the hexameric structure. Sodium ions balance out the negative charge of the phosphate groups.
SHMP exists as a white powder that is soluble in water. In aqueous solutions, it dissociates into linear polyphosphate chains and sodium ions. The linear polyphosphate chains can contain anywhere from three to over a hundred (PO3) repeating units. This gives SHMP the ability to sequester metal ions through its multiple phosphate binding sites.
Applications of Sodium Hexametaphosphate
Meat Processing
One of the largest uses of SHMP is in meat processing where it serves as a preservative and tenderizer. Its ability to bind calcium, magnesium, and iron ions prevents the formation of insoluble complexes that could cause meat to become tough after cooking. SHMP helps retain water in meat to keep it juicy and tender. It is approved by the FDA for use in processed meats up to certain concentration limits.
Detergents and Cleaning Products
SHMP acts as a builder in laundry and automatic dishwashing detergents. As a polyphosphate, it can sequester calcium, magnesium, and heavy metal ions found in hard water that would otherwise form precipitates and reduce cleaning ability. The chelating effect of SHMP helps keep these ions dispersed and guarantees maximum cleaning performance.
SHMP is also used for industrial and institutional cleaning, as well as in some dishwasher rinse aids. Due to its environmental impact, some places have restricted its use in household laundry detergents.
Water Treatment
Polyphosphates such as SHMP are used to control hardness, turbidity, corrosion and scaling in industrial water systems. As a sequestrant, SHMP prevents calcium and magnesium from binding onto pipe surfaces, boilers, heat exchangers and other equipment to deposit scale. It also inhibits corrosion by binding metal ions.
SHMP promotes the dispersal of suspended solids in raw water, allowing them to be more effectively removed via coagulation and filtration processes. This improves the clarity and quality of treated water.
Other Applications
- Dyeing and Printing: SHMP acts as a dispersing agent in textile dyeing and printing applications.
- Food Processing: It is used as a firming agent in canned foods to retain texture and as an emulsifier in processed cheese.
- Oil Well Drilling: SHMP reduces water loss into formations by inhibiting deposits in drilling mud systems.
- Concrete Additive: Slows setting and increases the workability of concrete mixes.
Properties and Regulations
SHMP has low toxicity with an oral LD50 in rats of over 4000 mg/kg. However, high levels can cause gastrointestinal issues in humans. It is a regulated substance due to concerns about phosphorus loading into the environment from wastewater. Many areas now restrict the content of SHMP in household cleaners. Manufacturers have started replacing it with newer metal complexes or alternate builders. Nonetheless, it remains widely used in industrial cleaners and for its other specialty applications.
In Summary, sodium hexametaphosphate is a versatile inorganic compound with excellent sequestrant properties due to its ability to bind multivalent metal cations like calcium. This has made it invaluable in numerous industries from food processing to detergents to water treatment. While environmental regulations will likely see it replaced domestically, SHMP will continue to play an important technical role globally for the foreseeable future.
Siddhi Gade
30 Blog posts