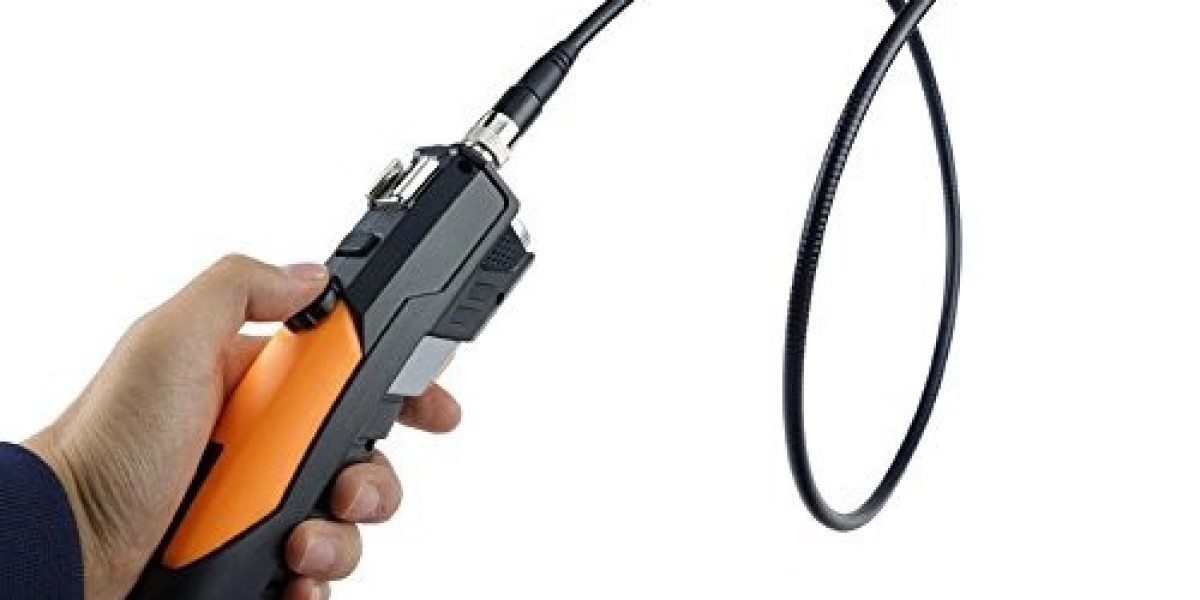
A video borescope is an optical inspection device that consists of a rigid or flexible insertion tube, camera module, video display screen, and lighting system. The insertion tube contains relay lenses or fiber optics bundles that transmit the light from the borescope's light source and the image signal from the camera back to the display screen. This allows the user to visually inspect the interior of an object or confined space.
Different Types of Video Borescopes
There are two main types of video borescopes: rigid and flexible. Rigid borescopes have stiff insertion tubes, making them well-suited for straight-line inspections of tubes, pipes, simple geometries, and other accessible areas. Flexible borescopes have non-rigid, bendable insertion tubes. This allows them to maneuver around tight corners and through complex shapes. Some flexible borescopes feature articulating joints along the insertion tube that enable improved maneuverability.
Rigid and semi-rigid borescopes are available in diameters as small as 1 mm, while flexible borescopes come in diameters from 1 mm up to around 15 mm. Larger diameters enable inspection of larger interior spaces but sacrifice the ability to access more confined areas. Both rigid and flexible borescopes are available with a wide variety of insertion tube lengths to suit different inspection requirements.
Applications in Industrial Inspections
Video borescopes have revolutionized inspections in many industrial applications. A key advantage is eliminating the need to disassemble equipment to visually inspect hard-to-reach interior areas.
Common industrial uses of video borescopes include:
- Aircraft engine inspections - Check turbine blades and interior passages without removing the engine from the aircraft.
- Power plant inspections - Inspect boiler tubes and other equipment without draining water and removing panels.
- Automotive inspections - View engine block and transmission areas through spark plug holes or other access points.
- Welding inspections - Check hard-to-see internal and circumferential welds on pipes, pressure vessels, and other structures.
- Manufacturing quality control - Visually inspect castings, molding cavities, and assembled components.
- Tunnel and pipeline inspections - Check concrete tunnels or pre-insulated pipe interiors for defects.
Video borescope technology allows issues to be identified earlier, reducing costly downtime compared to waiting for equipment disassembly. Inspections are also safer when there is no need for confined space entry.
Improving Industrial Processes with Real-Time Inspection
Beyond traditional inspections, borescopes enable new process monitoring and quality control applications. Some examples include:
- Observing powder coating applicators in real-time to improve coating uniformity.
- Monitoring welding and additive manufacturing processes to identify defects immediately.
- Checking plastic injection mold filling and venting during production runs.
- Guiding repairs on difficult-to-access internal structures like aircraft wings or wind turbine blades.
- Training and education by allowing students and technicians to view real industrial processes up close.
With integrated camera recording capabilities, borescopes provide documentation needed for quality audits, failure analysis, and process validation. Livestreaming inspection videos also allows remote expertise to be utilized.
Meeting Tougher Demands with Advanced Borescope Designs
As industrial needs evolve, borescope technologies likewise continue to progress. Newer designs improve optical performance, maneuverability, and durability to handle more challenging applications.
Some examples of innovative borescope technologies include:
- High-definition and ultra-high-definition camera systems for clearer, sharper images.
- Ruggedized insertion tubes offering increased flexibility, torque, crush resistance and cleaning ability.
- Patented multi-axis steering mechanisms and controlled flexion zones for superior maneuvering ability.
- Laser-based and alternative lighting technologies to better illuminate areas and identify surface defects.
- IP67 and IP68 waterproof models for wet environments up to full submersion.
- Small micro borescope diameters down to 1 mm or less for minimally invasive inspections.
Advanced borescope designs allow traditional industrial inspections to expand into even more difficult applications.
Get More Insights: Video Borescopes
Explore More Article: Water Turbine Market
About Author:
Alice Mutum is a seasoned senior content editor at Coherent Market Insights, leveraging extensive expertise gained from her previous role as a content writer. With seven years in content development, Alice masterfully employs SEO best practices and cutting-edge digital marketing strategies to craft high-ranking, impactful content. As an editor, she meticulously ensures flawless grammar and punctuation, precise data accuracy, and perfect alignment with audience needs in every research report. Alice's dedication to excellence and her strategic approach to content make her an invaluable asset in the world of market insights.
(LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/alice-mutum-3b247b137 )