Propanol is the most common type of alcohol. The chemical formula of propanol is CH3CH2CH2OH. Propan-1-ol, n-propanol, Propan-1-ol or n-propanol are the names of this colorless oil.
Alcohols are a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of one, two, or more hydroxyl groups (- OH) that are connected to carbon atoms in alkyl or hydrocarbon chains.
Propyl alcohol is used as solvent in medicine, floor polish, dental lotion, paint, printing ink, natural gum, pigment, intermediate, dye solution, Antifreeze, gasoline additive, paint additive and degreasing liquid. Propanol has low acute toxicity to animals when administered by skin, inhalation or Oral administration; It does not irritate the skin and is expected to absorb slowly in the dermis. N-propanol is easily metabolized and has no carcinogenic or mutagenic properties.
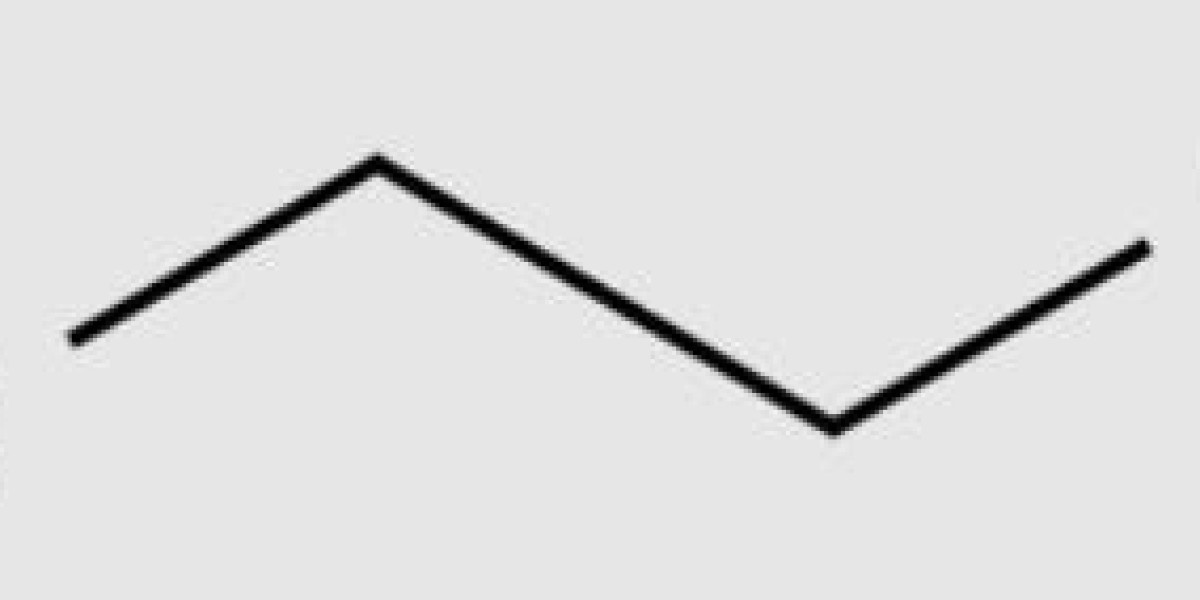
Propyl alcohol structure
Propanol is the most common type of alcohol. The chemical formula of propanol is CH3CH2CH2OH. Propan-1-ol, n-propanol, 1-propanol or n-propanol are the names of this colorless oil.
IUPAC name - Propane-1-ol
Preparation of propanol
From propanal
The catalytic hydrogenation of propionaldehyde produces Propan-1-ol. Propional is produced by hydroformylation of ethylene with carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas in the presence of catalysts such as cobalt octacarbonyl or rhodium complexes in the oxygen phase.
H2c=ch2+co+h2 → ch3ch2ch=o
Ch3ch2ch=o+h2 → ch3ch2ch2oh
The synthesis of methanol (methanol) from carbon monoxide and hydrogen produces propanol as a byproduct. It can also be found in fuel. It is most commonly used as a solvent for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, as well as paint preparations. Propanol is a colorless, flammable, aromatic liquid that is miscible with water in various proportions and has moderate toxicity.
The difference between n-propanol and isopropanol
Propanol, also known as n-propanol or Propan-1-ol, is one of the two isomeric alcohols used as solvents and intermediates in chemical processing. Isopropanol is the second isomer (Isopropyl alcohol).
Positional isomerism can be observed in n-propanol and isopropanol. The conformational isomers have the same carbon skeleton and functional groups, but the functional groups are located in different positions. The hydroxyl group appears on the first C atom of n-propanol. Hydroxyl groups exist on the second C atom of isopropanol. When heated with I2 and NaOH solutions, isopropanol produces a yellow iodoform precipitate, while n-propanol does not.
1-Butanol, primary alcohol, 2-butanol, secondary alcohol, 2-methyl-2-propanol, tertiary alcohol and phenol are four known alcohols. Propan-1-ol, Isopropyl alcohol, 2-methyl-2-butanol and p-chlorophenol are four potentially unknown alcohols.