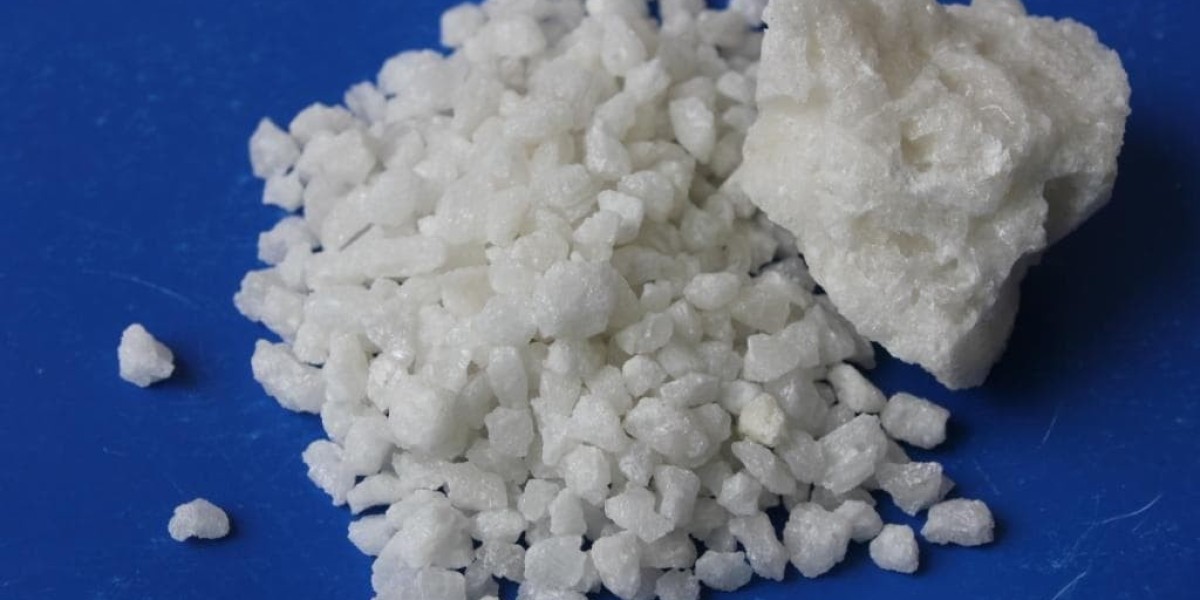
In the landscape of refractory materials, high alumina aggregates stand out for their remarkable resilience and versatility. These aggregates, composed primarily of alumina and other refractory minerals, exhibit exceptional thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making them indispensable in high-temperature applications across various industries.
High Alumina Aggregate are renowned for their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, making them ideal for use in applications where conventional materials would fail. With high melting points and excellent thermal shock resistance, high alumina aggregates can withstand rapid changes in temperature without experiencing damage or degradation. This resilience makes them well-suited for lining furnaces, kilns, reactors, and other equipment in industries such as steelmaking, cement production, and glass manufacturing, where temperatures can exceed 1,500°C (2,732°F).
One of the key advantages of high alumina aggregates is their superior chemical resistance, which allows them to withstand the corrosive effects of molten metals, slag, and abrasive materials. This resilience makes them essential for protecting equipment and extending its lifespan in harsh operating environments. In steelmaking, for example, high alumina aggregates are used to line ladles, tundishes, and torpedo cars, where they provide a protective barrier against the corrosive effects of molten steel and slag, ensuring the integrity of the refractory lining and prolonging equipment life.
Moreover, the landscape of high alumina aggregates is characterized by their versatility and adaptability to a wide range of applications and performance requirements. High alumina aggregates come in various grades and formulations tailored to specific industries, processes, and operating conditions. For example, in the cement industry, high alumina aggregates with high density and abrasion resistance are used to line rotary kilns and preheaters, where they are exposed to abrasive materials and high temperatures. In contrast, in the glass industry, high alumina aggregates with low iron content are preferred for lining glass tanks and furnaces, where they minimize impurities and improve glass quality.
Furthermore, the landscape of high alumina aggregates is evolving with advancements in manufacturing technologies and production processes. Innovations such as rotary kiln calcination, sintering, and granulation enable manufacturers to produce high-quality aggregates with precise control over composition, particle size distribution, and microstructure. Additionally, investments in research and development are driving the development of novel formulations and compositions of high alumina aggregates optimized for specific industries and applications, further enhancing their performance and versatility.
Get more insights on High Alumina Aggregate