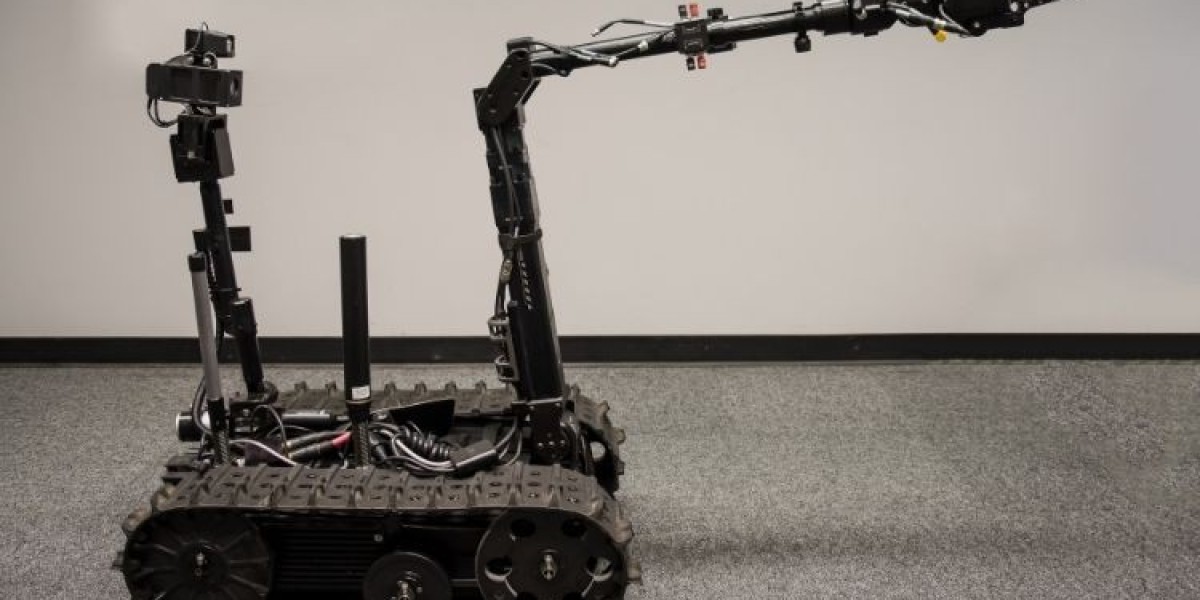
The global search and rescue robots market size reached approximately USD 22.39 billion in 2023. The market is further projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.0% between 2024 and 2032, reaching a value of USD 101.01 billion by 2032. In recent years, advancements in robotics technology have revolutionized search and rescue operations, enhancing the speed, efficiency, and safety of emergency response efforts. This blog post explores the evolution of search and rescue robotics, the types of robots used, key innovations driving the industry, and the benefits and challenges associated with these technologies.
Evolution of Search and Rescue Robotics
Search and rescue operations have traditionally relied on human responders, often putting them in dangerous or challenging situations. The use of robotics in such operations dates back to the early 20th century, with the development of remote-controlled vehicles for military and exploration purposes. However, it was not until the late 20th century that robotics began to play a significant role in search and rescue missions.
Advancements in technology, particularly in the fields of sensors, communication, and artificial intelligence (AI), have fueled the development of sophisticated search and rescue robots. These robots are capable of navigating complex environments, detecting survivors through various means, and communicating with human operators in real time.
Types of Search and Rescue Robots
Search and rescue robots can be classified into several categories based on their design and intended use. Ground robots, such as wheeled and legged robots, are used for navigating rough terrain and accessing areas inaccessible to human responders. Aerial robots, including drones and helicopters, provide a bird's eye view of the disaster zone, aiding in reconnaissance and surveillance efforts. Underwater robots, such as Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) and Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs), are used for search and rescue operations in aquatic environments.
Innovations in Search and Rescue Robotics
Several key innovations have propelled the field of search and rescue robotics forward. Sensors and imaging technology, such as thermal cameras and LIDAR, enable robots to detect and locate survivors in challenging environments, including dark or obscured areas. Communication and mapping capabilities allow robots to relay vital information to human operators and navigate complex environments autonomously.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being used to enhance the capabilities of search and rescue robots. These technologies enable robots to analyze data in real time, identify patterns, and make informed decisions, such as prioritizing areas for search or avoiding obstacles. Mobility and adaptability features, such as articulated limbs and interchangeable tools, allow robots to navigate diverse terrain and perform a variety of tasks, such as moving debris or delivering supplies.
Case Studies
The effectiveness of search and rescue robots has been demonstrated in several real-world scenarios. For example, during the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011, robots were used to access areas of the damaged nuclear plant that were too dangerous for human responders. Similarly, during Hurricane Katrina in 2005, drones were used to survey the extent of the damage and identify areas in need of urgent assistance. More recently, in the aftermath of the Nepal earthquake in 2015, robots were deployed to search for survivors trapped in collapsed buildings.
Benefits of Search and Rescue Robotics
Search and rescue robots offer several key benefits over traditional methods. They can access areas that are too dangerous or difficult for human responders, reducing the risk to human lives. They can also operate in harsh or hazardous environments, such as collapsed buildings or contaminated areas, where human intervention may be limited. Additionally, search and rescue robots can work around the clock, providing continuous support to emergency responders.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their potential benefits, search and rescue robots face several challenges. Cost and accessibility remain major barriers to widespread adoption, particularly in developing countries or regions with limited resources. Integration with existing emergency response systems and coordination with human responders are also key challenges that need to be addressed.
Looking ahead, the future of search and rescue robotics looks promising. Advances in technology, such as the development of smaller and more agile robots, improved sensors, and AI capabilities, are expected to further enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of search and rescue operations. Additionally, increased collaboration between researchers, developers, and emergency responders is key to overcoming the challenges and realizing the full potential of search and rescue robotics.
Innovations in search and rescue robotics are transforming emergency response efforts around the world. The evolution of robotics technology, coupled with advancements in sensors, communication, and AI, has enabled the development of sophisticated robots capable of navigating challenging environments and locating survivors in disaster zones. While challenges remain, the future of search and rescue robotics looks promising, with the potential to save lives and improve the effectiveness of emergency response operations.