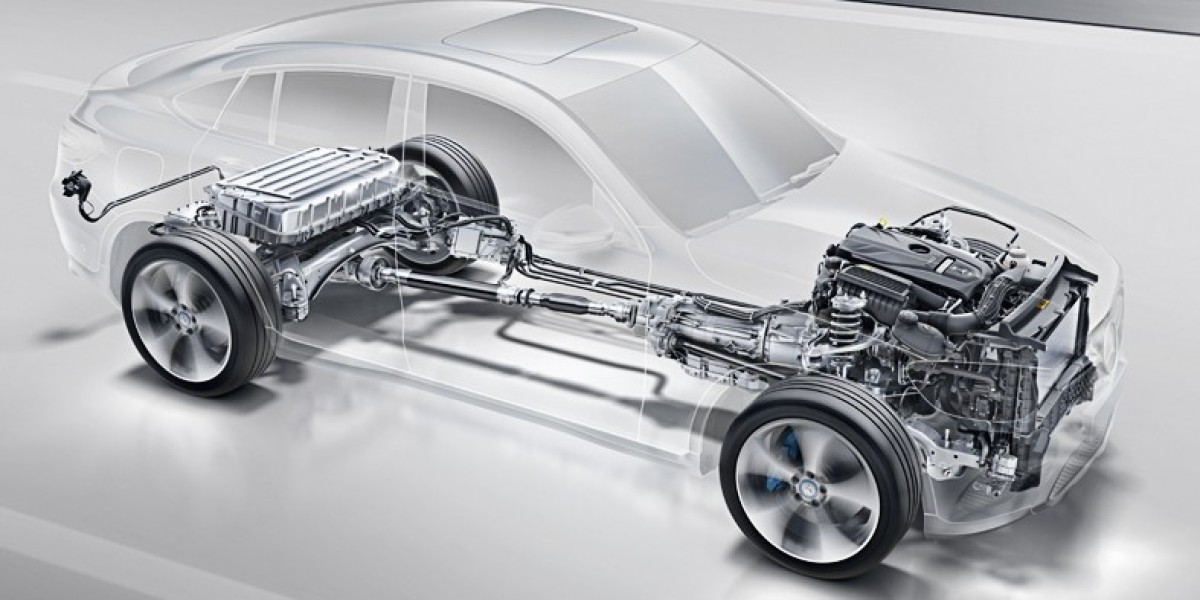
How All Wheel Drive Works
All wheel drive, also known as 4WD or AWD, refers to a vehicle transmission system that delivers power to all four wheels of a vehicle simultaneously for improved traction in various weather and road conditions compared to two-wheel drive vehicles where power is delivered to only two wheels. In an AWD system, a transfer case mechanism distributes torque between front and rear axles through a center differential. This allows for different rotation speeds between the front and rear axles to accommodate corners and turns. Some key components of a typical AWD system include the transfer case, center differential, front differential, rear differential, viscous coupling, and locking center differential.
Improved Traction and Control
One of the biggest advantages of AWD over two-wheel drive is its improved traction capability. Having power delivered to all four wheels means the vehicle can power through a variety of surfaces, from wet or slippery roads to light off-road conditions, much more effectively. This comes in very handy during inclement weather like rain, snow, or ice where traction can be compromised leading to reduced control and higher risks of skidding or getting stuck. The even weight distribution of AWD also provides better stability when cornering or braking on low grip surfaces.
Higher Payload Capacity
AWD systems allow vehicles to carry and tow heavier payloads than similar two-wheel All Wheel Drive vehicles. The extra traction means the vehicle can maintain control even when loaded to its maximum capacity. This makes AWD variants of trucks, SUVs, and cargo vans very popular for utility tasks that require carrying heavy equipment or towing trailers in varied weather conditions. The towing capacities of AWD vehicles are often several hundred pounds higher than 2WD models, expanding their commercial usage.
Improved Fuel Efficiency
While the added components may negatively impact fuel economy under some circumstances, advances in AWD technology have led to significant efficiency improvements. Modern AWD systems are more optimized with features like disconnecting drive shafts during highway cruising to reduce parasitic losses. They also allow for more precise traction control to prevent unnecessary power delivery to wheels with adequate traction. Lightweight materials help offset the weight impact. Overall, the fuel efficiency penalty of AWD compared to two-wheel drive has reduced to 5-10% on newer vehicles.
Enhanced Performance Driving
For performance-oriented drivers, the benefits of AWD go beyond just improving traction. The more even torque distribution allows for quicker acceleration from a standing start, faster sprint times, and higher cornering capabilities. AWD vehicles can launch harder from traffic lights and corners without losing traction. This makes for a more agile and nimble driving experience. Many high-performance cars now even come with advanced active AWD systems or torque vectoring abilities for precision handling.
Standard Safety Features
Advanced AWD setups frequently integrate with standard safety features like electronic stability control, traction control and anti-lock braking systems to enhance the braking and steering response. These systems monitor wheel speeds, throttle position, steering angle and other parameters to interject automatic traction and stability control interventions to maintain control in slippery conditions. The vehicle's on-board computer can also sense when individual wheels are starting to slip and preemptively apply brakes or reduce engine torque to maintain a straight travel path.
Increasing Adoption Across Vehicle Segments
While AWD was once mainly found on larger SUVs and luxury vehicles, the technology is becoming increasingly ubiquitous across different vehicle categories today. Compact and mid-sized SUVs, hatchbacks, sedans and pickup trucks now commonly offer AWD variants to appeal to diverse customer demands, especially in colder climates. Automakers are also able to package the components more efficiently at reduced costs. As capability features like towing capacity and traction control become more important selling points, AWD option take rates continue rising across the industry.
Lower Resale Values
One potential downside of AWD is its impact on the vehicle's residual value after a few years. Since the system adds complexity and hundreds of dollars to the upfront sticker price, those extra costs tend to remain with the used vehicle as well when calculating its trade-in or private sale worth. Higher maintenance requirements could also raise ownership costs slightly over the long run. However, the fuel economy gap is narrowing and capability upgrades provide offsetting value for many buyers. Overall resale values still depend more on make/model/trim demand trends in the used car marketplace.
Get more insights on All Wheel Drive
Also read related article on All Wheel Drive

![GoDaily Reviews: [Acid Reflux] How To Take Go Daily?](https://thewion.com/upload/photos/2021/01/NAq1ioEeLjk7orB51OgD_27_a0dfafc203e4951187caeee3d8c4aa76_image.jpg)