Insect growth regulators (IGRs) are chemical substances designed to interfere with the growth and development of insects, ultimately reducing their populations. Unlike traditional pesticides that typically kill insects upon contact, IGRs work by mimicking or inhibiting hormones in insects, affecting their ability to mature, reproduce, or molt. This approach is often more targeted and environmentally friendly compared to conventional insecticides, as IGRs tend to have minimal effects on non-target species, including humans, animals, and beneficial insects like bees.
IGRs are a crucial tool in integrated pest management (IPM) programs, offering an alternative that helps delay the development of resistance in insect populations while reducing reliance on toxic chemicals. By disrupting life cycles rather than killing adult insects immediately, IGRs are especially effective in long-term pest control strategies, particularly for managing populations of pests such as mosquitoes, fleas, and cockroaches.
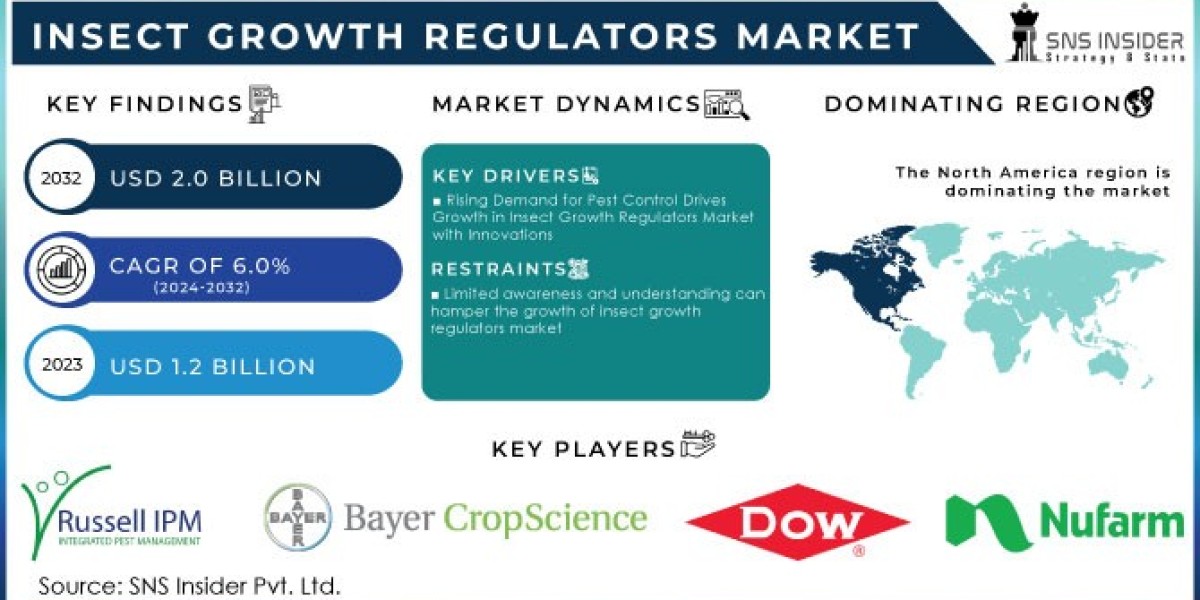
The Insect Growth Regulators Market Size was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 2.0 billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 6.0% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
How Insect Growth Regulators Work
Insect growth regulators function by disrupting the hormonal systems that regulate insect development. Depending on the type of IGR, they may prevent larvae from progressing to the pupal stage, inhibit the emergence of adult insects, or prevent reproduction. Common classes of IGRs include juvenile hormone analogs, chitin synthesis inhibitors, and ecdysone inhibitors.
Juvenile Hormone Analogs (JHAs): These IGRs mimic juvenile hormones in insects, preventing them from reaching maturity. When larvae are exposed to JHAs, they remain in the juvenile stage and are unable to develop into reproductive adults. Over time, this reduces the overall population as the larvae fail to transition into breeding adults.
Chitin Synthesis Inhibitors: Chitin is a key component of an insect's exoskeleton. Chitin synthesis inhibitors prevent insects from producing this critical structural material, causing deformities in their exoskeleton or interrupting their ability to molt. Without a proper exoskeleton, insects either die or fail to progress through their normal developmental stages.
Ecdysone Inhibitors: Ecdysone is a hormone that controls molting and metamorphosis in insects. Ecdysone inhibitors prevent the insect from molting, causing them to remain in their immature stage, and leading to death over time due to developmental arrest.
Advantages of Insect Growth Regulators
One of the key benefits of IGRs is their selectivity. Because they specifically target the endocrine systems of insects, they are generally considered safer for the environment and non-target organisms compared to conventional insecticides. This makes them suitable for use in a wide range of settings, from agriculture and forestry to urban pest management.
IGRs also tend to have a lower risk of fostering insect resistance than traditional insecticides. Resistance to insecticides occurs when a small percentage of the population survives exposure and passes on their resistant traits. Because IGRs work through hormonal disruption rather than direct poisoning, it is more difficult for insect populations to develop resistance to these chemicals.
Insect growth regulators are also long-lasting. While traditional insecticides may need to be reapplied frequently, IGRs can continue working for extended periods, especially when applied to breeding areas or larval habitats. This longevity contributes to their cost-effectiveness and efficacy in long-term pest control programs.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their many advantages, the use of insect growth regulators is not without challenges. One of the primary drawbacks is that IGRs are slower-acting than conventional insecticides. They do not immediately kill adult insects, meaning that users may not see the rapid population reduction associated with other chemicals. This slower mode of action may require a more patient and sustained approach to pest management.
Additionally, IGRs may not be effective against all types of pests. Their effectiveness is largely dependent on the timing of application. For instance, IGRs need to be applied at specific stages of the insect life cycle to be effective. If applied too late, when the pests have already reached adulthood, they may have little impact.
Moreover, while IGRs are generally safe for non-target organisms, their application in certain environments requires careful consideration. For instance, they should not be used in areas where sensitive aquatic ecosystems could be inadvertently exposed to runoff.
Market Trends and Growth Drivers
The increasing adoption of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies and the growing need for sustainable agriculture are major factors driving the demand for insect growth regulators. Farmers and pest control professionals are seeking safer, more targeted solutions that minimize environmental harm while effectively managing pest populations.
In agricultural settings, IGRs are being increasingly used as part of an overall strategy that combines biological controls, cultural practices, and selective chemical interventions. This integrated approach is gaining popularity due to its ability to manage pests while reducing the use of broad-spectrum insecticides, which can negatively impact beneficial insects and pollinators.
Additionally, the growing concern over pesticide resistance is pushing the development of more innovative pest control solutions. As insecticide resistance continues to rise globally, IGRs provide an alternative mechanism of action that can be integrated into resistance management programs.
Conclusion
Insect growth regulators represent a significant advancement in pest management by offering a more sustainable and selective approach to controlling insect populations. With their ability to disrupt insect development and reduce populations over time, IGRs are a vital component of integrated pest management strategies. As environmental concerns and pesticide resistance issues continue to grow, IGRs are likely to play an increasingly important role in global pest control efforts.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)