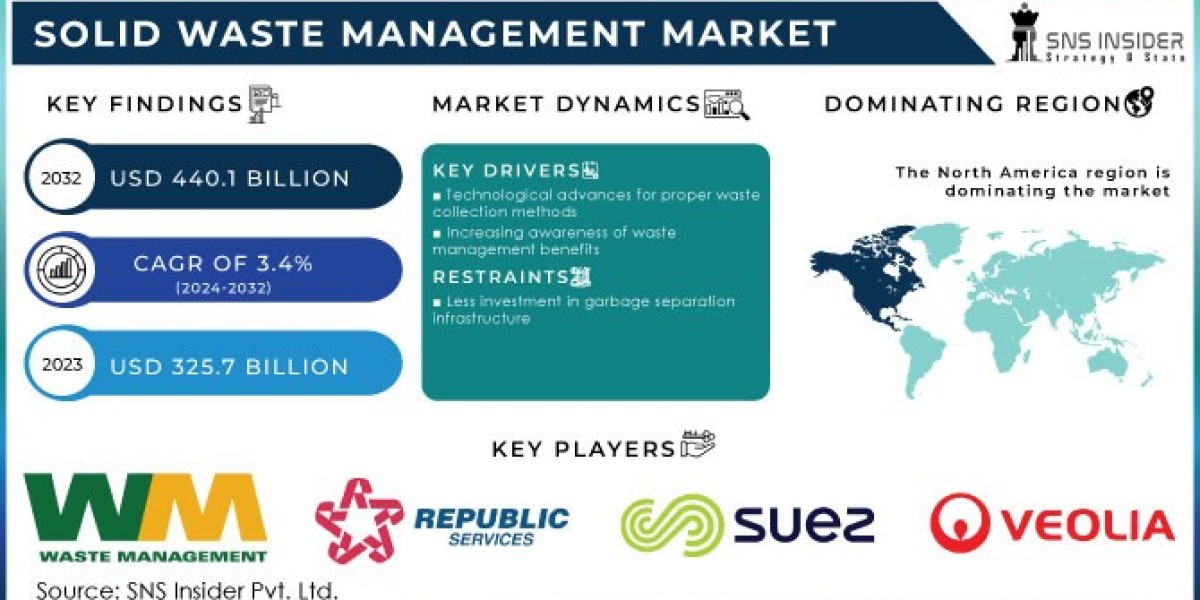
Solid waste management involves the systematic handling of waste materials generated by human activities. Effective management of these materials is essential to protect public health, reduce environmental impact, and ensure the sustainability of urban and rural areas. The process encompasses a series of actions, including waste collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal. The Solid Waste Management Market Size was valued at USD 325.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 440.1 billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 3.4% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Historical Context and Evolution
Historically, waste management practices were relatively simple, focusing primarily on collection and disposal. In ancient civilizations, waste was often dumped into open pits or rivers, leading to significant environmental and health problems. With the industrial revolution and urbanization, waste management became more complex, requiring organized systems to handle increasing volumes of waste.
The 20th century saw significant advancements in waste management, including the development of sanitary landfills, incineration technologies, and recycling programs. These innovations aimed to address the growing challenges of waste disposal and environmental protection.
Modern Approaches to Waste Management
Today, solid waste management is characterized by a more sophisticated and integrated approach. Modern practices focus on reducing waste generation, enhancing recycling efforts, and adopting sustainable disposal methods. Key components of modern waste management include:
- Integrated Waste Management Systems: These systems combine various waste management practices to achieve optimal results. By integrating waste reduction, recycling, and disposal, municipalities can effectively manage waste and minimize environmental impact.
- Source Separation: Encouraging individuals and businesses to separate waste at the source facilitates recycling and reduces contamination. Source separation involves separating recyclables, organics, and non-recyclables, making it easier to process and manage waste.
- Green Waste Technologies: Advances in green waste technologies, such as composting and anaerobic digestion, are transforming how organic waste is handled. These technologies convert organic materials into valuable resources, such as compost and biogas, contributing to sustainability.
- Waste-to-Energy: Waste-to-energy technologies, including incineration and gasification, convert waste into energy, reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills and providing a renewable energy source. These technologies are becoming increasingly important as a means of managing non-recyclable waste.
Economic and Environmental Impacts
Effective waste management has significant economic and environmental impacts. Economically, efficient waste management can reduce costs associated with waste collection, transportation, and disposal. By minimizing waste generation and maximizing recycling, municipalities can lower overall waste management expenses.
Environmentally, proper waste management practices help reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and mitigate the effects of climate change. For example, recycling reduces the need for raw materials, decreases energy consumption, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges and Opportunities
The solid waste management sector faces several challenges, including:
- Population Growth: Increasing populations and urbanization contribute to higher waste generation, placing pressure on waste management systems. Developing scalable and efficient solutions is essential to address this challenge.
- Waste Composition: The composition of waste is evolving, with an increase in electronic waste (e-waste), hazardous materials, and mixed waste streams. Adapting waste management practices to handle diverse and complex waste types is crucial.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about waste reduction, recycling, and responsible disposal is essential for successful waste management. Increasing awareness and engagement can lead to higher participation rates and better waste management outcomes.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in modern waste management infrastructure, including recycling facilities, waste-to-energy plants, and advanced sorting technologies, is necessary to keep pace with growing waste volumes and evolving waste streams.
Future Directions in Solid Waste Management
The future of solid waste management is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
Circular Economy: Emphasizing the principles of the circular economy, which focuses on reducing waste and maximizing resource efficiency, will become increasingly important. This approach aims to close the loop on material use and reduce environmental impact.
Technological Innovations: Advances in technology, such as artificial intelligence (AI) for waste sorting and blockchain for tracking waste, will enhance the efficiency and transparency of waste management systems.
Policy and Regulation: Governments and regulatory bodies are expected to implement stricter waste management policies and regulations, promoting sustainability and encouraging innovation in the sector.
Community Engagement: Engaging communities in waste reduction and recycling initiatives will be crucial for achieving long-term waste management goals. Public participation and education will drive positive behavioral changes and improve overall waste management outcomes.
Conclusion
Solid waste management is an evolving field that requires continuous innovation and adaptation to address the growing challenges of waste generation and environmental impact. By embracing modern practices, advancing technologies, and fostering public engagement, communities can achieve more effective and sustainable waste management. As the global population and urbanization continue to rise, the importance of efficient waste management solutions will only increase, underscoring the need for ongoing investment and innovation in this essential sector.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)