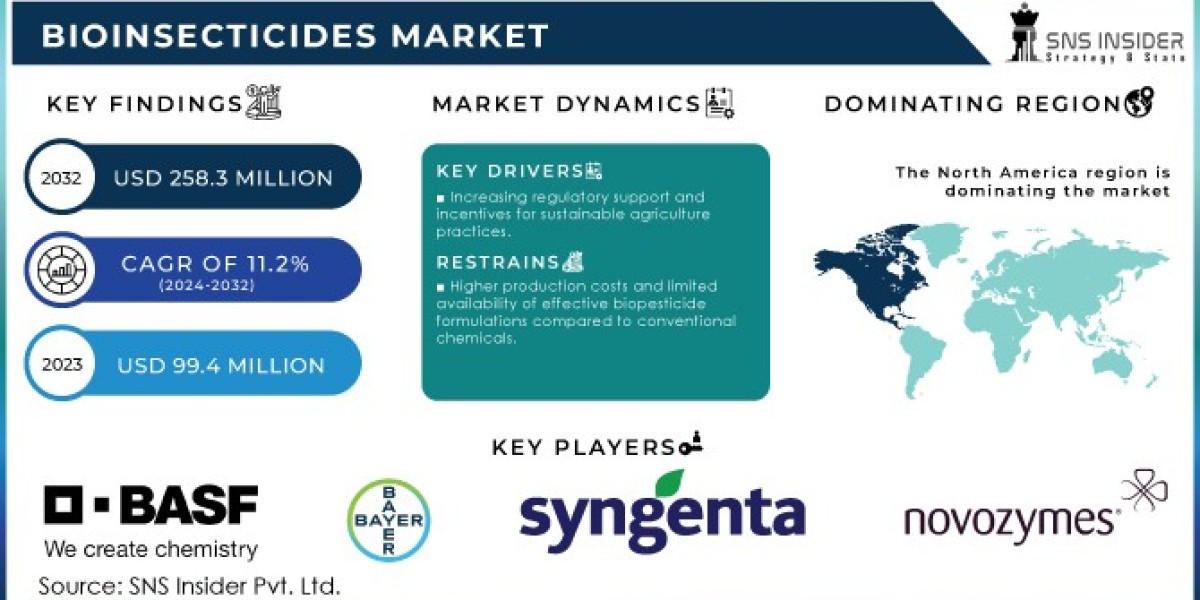
Bioinsecticides, derived from natural substances like microorganisms, plants, or minerals, are transforming the agricultural industry by offering a more sustainable and environmentally friendly solution for pest control. Unlike chemical insecticides, which can harm non-target species and the environment, bioinsecticides focus on specific pests, reducing collateral damage and promoting healthier ecosystems. The Bioinsecticides Market Size was valued at USD 99.4 million in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 258.3 million by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 11.2% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Types of Bioinsecticides and Their Mechanisms
Bioinsecticides are classified into several types based on their source and mode of action. These include microbial bioinsecticides, botanical bioinsecticides, and biochemical bioinsecticides.
- Microbial Bioinsecticidesuse microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses that are pathogenic to insects. For instance, bacteria like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) are commonly employed to target caterpillars, beetles, and flies. When ingested by the insect, Bt produces toxins that damage the insect’s gut, ultimately leading to death.
- Botanical Bioinsecticidesare derived from plants with insecticidal properties. Neem oil is one of the most widely recognized plant-based bioinsecticides. It works by interfering with the feeding, growth, and reproduction of insects, making it highly effective against a wide range of pests.
- Biochemical Bioinsecticidesinclude substances like pheromones or hormones that disrupt the lifecycle or behavior of insects. For example, pheromones can be used to lure insects into traps or prevent them from mating, thereby reducing pest populations over time.
These various bioinsecticides work by specifically targeting insect pests, thus minimizing the impact on non-target organisms such as beneficial insects, pollinators, and wildlife.
The Bioinsecticides Market Size was valued at USD 99.4 million in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 258.3 million by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 11.2% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Advantages of Using Bioinsecticides
The use of bioinsecticides offers numerous advantages over traditional chemical insecticides, making them a key component of sustainable agriculture. One of the most important benefits is their environmental safety. Since bioinsecticides are derived from natural organisms, they are biodegradable and do not leave harmful residues in the environment. This is particularly important in areas where water and soil contamination from chemical pesticides is a concern.
Bioinsecticides also help to prevent the development of insect resistance, a common problem with chemical insecticides. Because bioinsecticides often target specific physiological or behavioral aspects of insects, pests are less likely to develop resistance. This selective action helps maintain long-term effectiveness, making bioinsecticides a reliable option for pest management.
In terms of human health, bioinsecticides are considered safer than chemical insecticides. They pose fewer risks to farmers, agricultural workers, and consumers who are exposed to treated crops. Furthermore, bioinsecticides are often used in organic farming systems, which are growing in popularity due to increased consumer demand for organic and pesticide-free produce.
Applications in Modern Agriculture
Bioinsecticides have found widespread application across various sectors of agriculture, including organic farming, horticulture, and field crops.
Organic Farming: In organic farming, bioinsecticides are essential due to the prohibition of synthetic chemicals. Farmers use bioinsecticides to control a wide range of pests while adhering to organic farming regulations. Products like Bt and neem oil are widely used to protect crops without compromising the organic status of the produce.
Horticulture: Horticultural crops such as fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants are particularly vulnerable to insect pests. Bioinsecticides offer an effective solution for managing these pests while maintaining the aesthetic and commercial value of the crops. For instance, neem oil is commonly used in the control of aphids and spider mites in greenhouses.
Field Crops: Large-scale agricultural operations, including those that cultivate corn, wheat, and soybeans, are increasingly incorporating bioinsecticides into their pest management strategies. The use of bioinsecticides in these crops helps reduce the environmental impact of farming while ensuring healthy yields.
Challenges and Limitations
While bioinsecticides offer numerous advantages, there are challenges that need to be addressed to increase their adoption. One of the primary limitations is their relatively short shelf life and degradation in field conditions. Many bioinsecticides break down quickly when exposed to sunlight, rain, or temperature fluctuations, reducing their effectiveness over time. This often requires more frequent applications, which can increase costs for farmers.
Another challenge is the slower action of bioinsecticides compared to chemical insecticides. Bioinsecticides often take several days to control pest populations, which may not be ideal in situations where rapid pest control is needed. Additionally, bioinsecticides may not always be as cost-effective as chemical insecticides, particularly in large-scale agricultural operations where higher volumes of bioinsecticides are required.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development are working to improve the stability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of bioinsecticides.
Future Outlook for Bioinsecticides
As the world moves toward more sustainable agricultural practices, the future of bioinsecticides looks promising. The increasing global demand for organic and eco-friendly food products is expected to drive the growth of the bioinsecticide market. Furthermore, government regulations aimed at reducing the use of chemical pesticides are likely to encourage more widespread adoption of bioinsecticides.
Innovations in biotechnology and microbial engineering are expected to lead to the development of more effective and resilient bioinsecticides. These advances could help overcome some of the current limitations, such as short shelf life and slow action, making bioinsecticides a more viable option for farmers around the world.
Conclusion
Bioinsecticides represent a critical advancement in pest management, offering a safe, eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical insecticides. As more farmers and agricultural companies adopt sustainable practices, bioinsecticides are poised to become an integral part of modern farming systems. With continued research and innovation, bioinsecticides will play a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability while ensuring the future of food security.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)