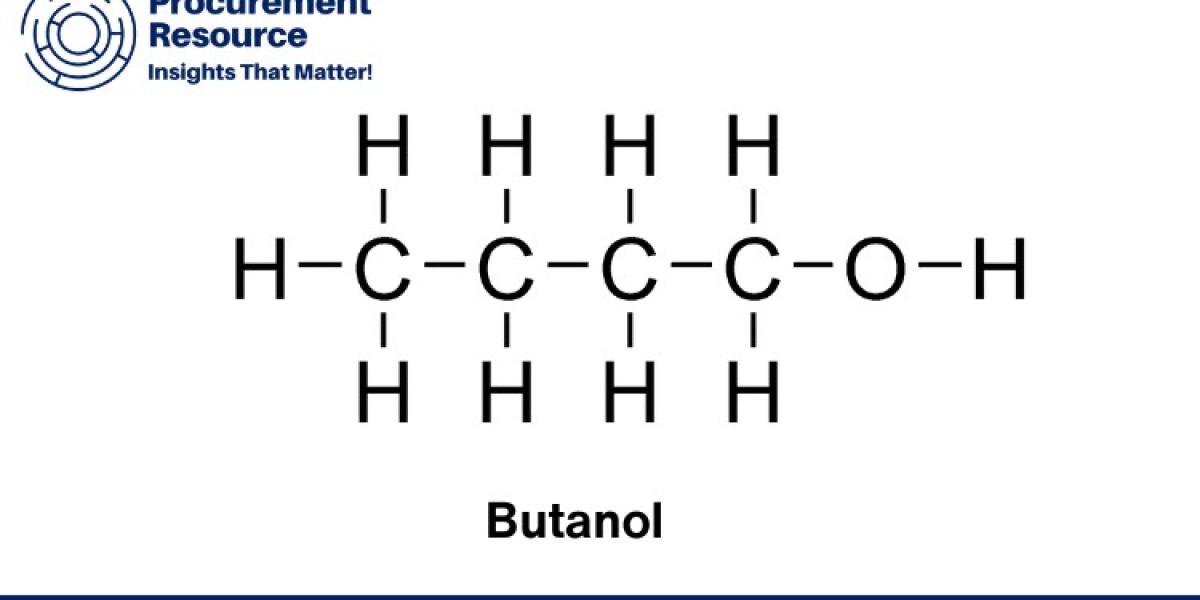
Butanol, a crucial industrial chemical, finds extensive use across a wide range of applications, including as a solvent, in the production of plastics, textiles, and in the automotive sector for fuel additives. Its production process is complex and can vary depending on the raw materials used, plant technology, and geographical location. The Butanol Production Cost is a critical aspect for manufacturers, as it directly influences pricing strategies, profitability, and market competitiveness. In this article, we will explore various elements that contribute to the cost of Butanol production, including cost models, pre-feasibility studies, industrial trends, labor charges, utilities, logistics, and the supply chain.
Understanding the Butanol Production Cost
The Butanol production cost is determined by several factors ranging from the choice of feedstock to operational processes and transportation costs. Typically, Butanol is produced via two major processes: the Oxo process (also known as hydroformylation) and the ABE (Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol) fermentation process. The cost of these processes varies considerably, and understanding these cost drivers is essential for industry players to remain competitive in the market.
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/butanol/request-sample
Cost Model for Butanol Production
The Butanol production cost model takes into account both fixed and variable costs incurred during production. Fixed costs include the initial capital investment required for setting up the plant, machinery, and infrastructure, whereas variable costs cover raw materials, labor, utilities, and other operational expenses.
Raw Materials: The selection of feedstock for Butanol production is one of the largest cost determinants. In the Oxo process, feedstocks like propylene and syngas are used, while the ABE process primarily relies on agricultural products such as corn and sugar for fermentation. The cost of raw materials fluctuates based on market conditions and geographic location.
Production Process: The production method plays a significant role in determining overall costs. The Oxo process is more capital intensive due to the need for high-pressure equipment and specialized catalysts. In contrast, the ABE fermentation process has lower capital expenditure but higher operational costs due to the complexity of fermentation and the need for specialized fermentation tanks.
Labor Costs: Labor is a crucial cost factor in Butanol production. Skilled labor is necessary for monitoring production, operating advanced machinery, and ensuring quality control. Labor costs also vary depending on the geographical location of the production facility, as regions with higher labor rates will contribute significantly to the overall cost.
Pre-feasibility Studies and Economic Viability
Before setting up a Butanol production plant, it is essential to conduct pre-feasibility studies to assess the economic viability of the project. These studies focus on various factors, such as market demand, capital investment, operational costs, and return on investment (ROI).
Pre-feasibility studies typically include:
- Market Analysis: Understanding demand trends and potential market expansion opportunities.
- Raw Material Availability: Analyzing the availability and cost of raw materials in the intended location.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assessing whether the plant can comply with local environmental regulations and safety standards.
- Energy Efficiency: Determining the energy consumption and identifying opportunities to reduce utility costs.
The insights gained from pre-feasibility studies help businesses make informed decisions regarding investments, site selection, and process optimization.
Industrial Trends Impacting Butanol Production Costs
Over the years, industrial trends have significantly impacted Butanol production costs. Some key trends include:
Shifts Toward Renewable Resources: With the global shift towards sustainability, companies are increasingly looking for renewable feedstocks for Butanol production. This shift can lower raw material costs in the long term but may require higher initial investments for setting up biorefineries.
Technological Advancements: New technological innovations, including improvements in catalytic processes and fermentation techniques, can lead to cost reductions by improving yield and energy efficiency. However, these technologies often come with high research and development (R&D) costs, which must be considered in the overall cost model.
Economies of Scale: As the demand for Butanol continues to grow, large-scale production facilities benefit from economies of scale. Large plants can reduce per-unit costs by increasing production volumes, which lowers the overall production cost.
Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations on emissions, waste disposal, and energy usage are driving up production costs. Manufacturers are investing in cleaner technologies and compliance processes, which often lead to higher operational costs but are necessary to avoid fines and maintain sustainable operations.
Labor Charges in Butanol Production
Labor costs are an essential component of the overall Butanol production cost. Highly skilled labor is required for managing complex production processes, especially in large-scale plants where monitoring and maintaining equipment is crucial. Labor charges can vary based on:
- Location: In regions with high living costs, labor charges can significantly impact the overall production cost.
- Skill Level: The more skilled and experienced the workforce, the higher the labor charges. Operators with advanced technical knowledge and expertise in chemical processes are necessary to ensure efficient production.
- Unionization: In some countries, labor unions may negotiate higher wages, which can increase labor-related expenses for manufacturers.
Utilities, Logistics, and Supply Chain Considerations
The cost of utilities such as electricity, water, and steam also contributes to the Butanol production cost. The energy-intensive nature of Butanol production means that energy consumption is one of the largest operational costs. Companies often explore energy-efficient solutions such as renewable energy sources to reduce utility costs.
In addition, logistics and supply chain management play a critical role in the cost structure. The transportation of raw materials to the production site, as well as the delivery of finished Butanol to markets, incurs significant logistics costs. Companies often optimize their supply chains to reduce transportation costs by sourcing raw materials locally or using bulk shipping options.
Supply Chain efficiency is crucial to ensuring that production is not disrupted due to material shortages or delays. Any inefficiencies in sourcing, inventory management, or distribution can lead to increased costs and reduced profitability.
Procurement Resource for Butanol Production
Effective procurement plays a vital role in controlling production costs. By sourcing high-quality raw materials at competitive prices, procurement teams can directly influence the cost structure of Butanol production. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers, negotiating bulk discounts, and leveraging global supply chains are essential strategies for reducing procurement costs. Businesses that strategically manage their procurement process can achieve better cost control and improve profitability.
Request a Free Sample
If you're interested in learning more about Butanol production costs, including detailed insights and customized cost models, we invite you to request a free sample of our comprehensive Butanol production cost report. Our report offers a deeper analysis of market trends, cost components, and strategies for cost optimization, helping you make more informed decisions in the Butanol production industry.
Request Your Free Sample Report - https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/butanol/request-sample
The Butanol production cost is influenced by numerous factors, including raw material prices, production processes, labor charges, and supply chain dynamics. Companies that understand these cost drivers and integrate strategic cost management measures can achieve more efficient production and maintain a competitive edge in the market. Additionally, pre-feasibility studies, industrial trends, and procurement resources all play a role in determining the economic viability of Butanol production. As market demands evolve and new technologies emerge, the Butanol production industry must continue to adapt to keep production costs under control and ensure profitability.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Endru Smith
Email: [email protected]
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada - Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK - Phone no: +44 7537171117 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) - Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address:30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA