Bromous acid is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula of HBrO2. It is an unstable compound, although its conjugated base bromine salt has been separated. In acidic solution, bromide is decomposed into bromine.
In 1905, Richards a H. The existence of bromous acid was proved by a series of experiments involving silver nitrate (AgNO3) and bromine. Excess cold water reacts to generate hypobromous acid (HBrO), silver bromide (AgBr) and nitric acid (HNO3):
Br2 + AgNO3 + H2O→HBrO + AgBr + HNO3
Richards found that adding excessive liquid bromine to concentrated silver nitrate (AgNO3) would lead to different reaction mechanisms. The ratio of oxygen to bromine is calculated according to the equivalent proportion of acid bromine formed in the previous reaction. The accurate value is O: Br (0.149975: 0.3745), indicating that the acid compound contains two oxygen atoms and one bromine atom. Therefore, the chemical structure of the acid compound is deduced as HBrO2.
Richards believed that hypobromous acid (HBrO) was produced by the reaction of bromine and silver nitrate solution:
Br2 + AgNO3 + H2O→HBrO + AgBr + HNO3
2 AgNO3 + HBrO + Br2 + H2O→HBrO2 + 2 AgBr + 2 HNO3
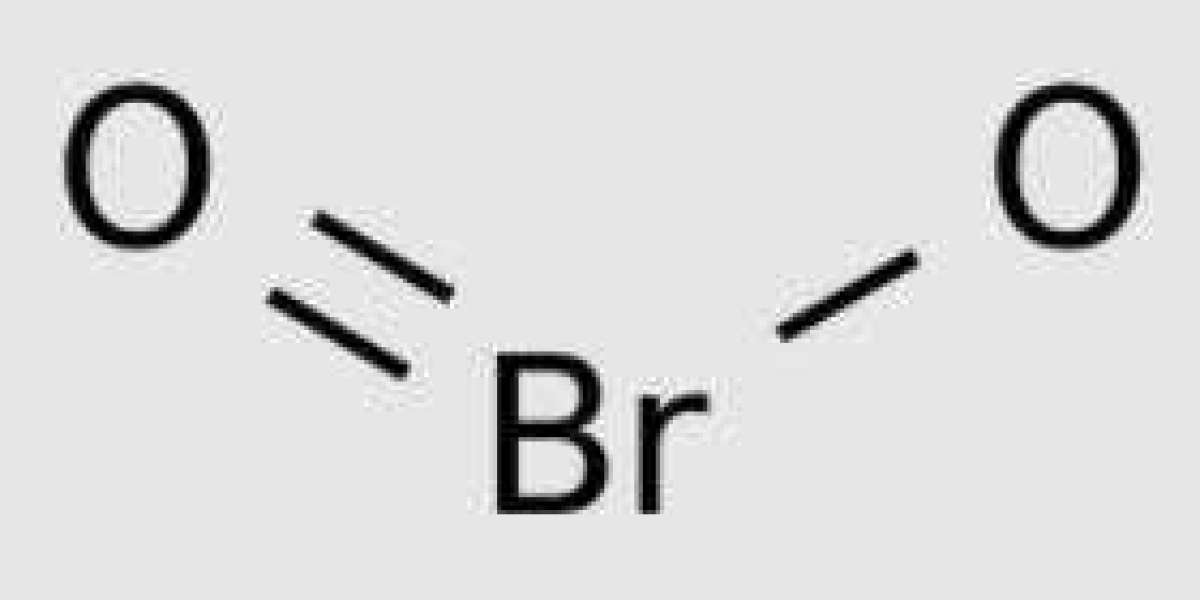
The molecule HBrO2 is a curved structure with ∠ (H − O − Br) angle of 106.1 °. HOBrO also adopts a non planar conformation, in which the dihedral angle ∠ (H − O − Br − O) of one isomer structure (2a) is 74.2 °. The planar structures of the other two isomers (2b cis and 2c trans) are transition states of rapid enantiomerization.
Another study found three isomers: HOOBr, HOBrO and HBr (O) O.
The NaBrO2 · 3H2O and Ba (BrO2) 2 · H2O salts were obtained by crystallization. After these aqueous solutions were treated with Pb2+, Hg2+and Ag+salts, the corresponding heavy metal bromide was precipitated in solid form.
bromous acid is the Belousov Zhabotinsky reaction product of potassium bromate, ceric sulfate (IV), malonic acid and citric acid in dilute sulfuric acid. bromous acid is the intermediate stage of the reaction between bromate ion (BrO − 3) and bromine (Br −):
BrO−3 + 2 Br−→HBrO2 + HBrO
Other relevant reactions in such oscillating reactions are:
HBrO2 + BrO−3 + H+→2 BrO2 + H2O
2 HBrO2→BrO−3 + HOBr + H+
Bromide reduces permanganate to manganate (VI):
2 MnO2−4 + BrO−2 + OH−→2 MnO2−4 + BrO−3 + H2O
The acid dissociation constant Ka=[H+] [BrO − 2]/[HBrO2] of bromous acid was determined by different methods.
In the study of bromous acid decomposition, pKa value of bromous acid was estimated. The decomposition rate of bromate was measured as a function of hydrogen and bromate ion concentration. With this method, pKa value of bromous acid is 6.25. [8]. 0
Another method was used to determine the pKa value of bromous acid based on the initial reaction rate of sodium bromide and potassium iodide at pH 2.9~8.0, 25 ℃ and ionic strength 0.06 m. The acid dissociation constant determined by this method is Ka=(3.7 ± 0.9) × 10−4 M, pKa = 3.43±0.05。
Bromate is a relatively weak nucleophilic reagent due to its low alkalinity compared with other oxidants (hypochlorite, anion of peroxide) with oxygen as the center. The rate constant of bromate to carbocation and acceptor substituted olefins is 1-3 orders of magnitude lower than that of hypobromate.