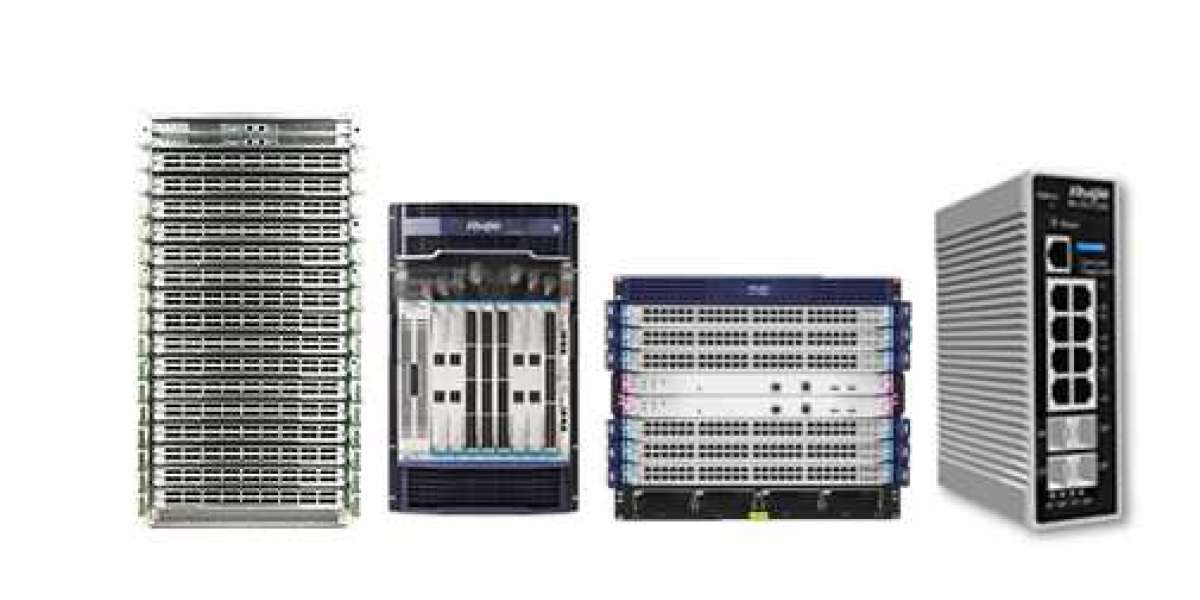
A network switch is a device that allows two or more IT devices (such as computers) to communicate with each other. Connecting multiple IT devices together can create a communication network. Computing, printing, servers, file storage, Internet access, and other IT resources can be shared over the network.
IT equipment communicates by exchanging "packets" on the network. Basic switches forward packets from one device to another, while more complex operations (such as determining whether a packet is allowed to reach its intended destination) have traditionally been the domain of other types of network devices.
Switches can be in the form of dedicated devices, or components of other devices such as network routers and wireless access points (aps) that operate on packets. The basic switching technology has existed for decades and is one of the basic building blocks of all modern IT networks (including the Internet).
What problem can the switch solve?
Network switches connect users, applications and devices in the network to realize communication and resource sharing between users. The simplest network switch only provides connections to devices on a single local area network (LAN). More advanced switches can connect devices from multiple LANs, and even include basic data security functions.
In more advanced switches, functions other than simple LAN interconnects are usually subsets of typical functions in other network devices, such as routers and firewalls. Although these switches have advanced features, they are still called "switches" because their primary purpose is to connect devices to each other as part of an IT network.
An important role of advanced switches is to be able to create "virtual networks". The virtual network isolates the network system groups from each other according to the configuration provided by the network administrator. This capability allows a large number of systems to be connected to a single physical network while securely separating some systems from others. Virtual network types include vpn (Virtual private network), vlan (Virtual lan), and evpn - vxlan (Ethernet VPN virtual eXtensible lan), which are generally used in large and medium-sized networks. EVPN-VXLAN is an increasingly common network segmentation implementation in modern enterprise networks.
Network switches come in a variety of speeds, functions, and sizes. They can support anywhere from three to thousands of devices. Multiple network switches can be connected together to support more devices. The details of how these switches are connected are called "network topology".
Using high-speed switches and modern "spikes" topology with high port density, tens of thousands of devices can be easily connected to a single physical network. In the spine leaf data center network, leaf switches aggregate traffic from servers and directly connect to the spine switches, which connect all leaf switches in a full mesh topology. These large networks are usually divided into a large number of virtual networks using EVPN-VXLAN, and leaf switches provide access (and routing) to different network segments.
This type of network is common in data centers shared by many customers (called "multi tenant" data centers) and used by governments and large enterprises.