Laser welding: micro welding of precision and complex parts
Medical devices are usually portable tools or small accessories, which are usually used for surgery or transplantation to the human body. The welding of these accessories is critical to the patient's health. Therefore, welding quality should be strictly controlled, including repeatable laser pulses; Small spot diameter and effective absorption of laser energy through materials are required. Generally, the welding process with penetration depth and spot size less than 1mm is called laser micro welding, which is generally used for cardiac pacemakers and surgical blades. It is used for precise welding of endoscope equipment, batteries and other products.
Laser micro welding can be divided into spot welding and seam welding: spot welding process is required for medical pipes, thin spring electric contacts, medical guide wires of hook shaped pieces and medical wave conductors. The spot welding process needs to accurately transmit the laser energy to the welding point, so an appropriate laser horn is required.
Suture welding is a sealing method of human transplantation equipment, which can be realized by pulsed Nd: YAG laser or CW laser. The specific laser used depends on the geometry of the weldment or the sensitivity of the material to heat.
Laser cutting: used to cut human transplantation equipment and surgical tools
In the field of medical devices, laser cutting includes implantable stents, endoscopes and arthroscopic tools, flexible shafts, needles, catheters and waveguides, as well as flat appliances, such as fixtures, which are critical to achieving advanced surgery and improving the health and quality of life of millions of patients.
Laser cutting of medical devices usually requires the use of pressurized auxiliary gas, usually oxygen, argon or nitrogen. The gas flows coaxial with the speed of light. The laser source for cutting is microsecond level, and nanosecond fiber laser or USP laser with pulse width of 100/s can be selected. Fiber laser is widely used because of its low price, good beam quality and easy integration with fiber.
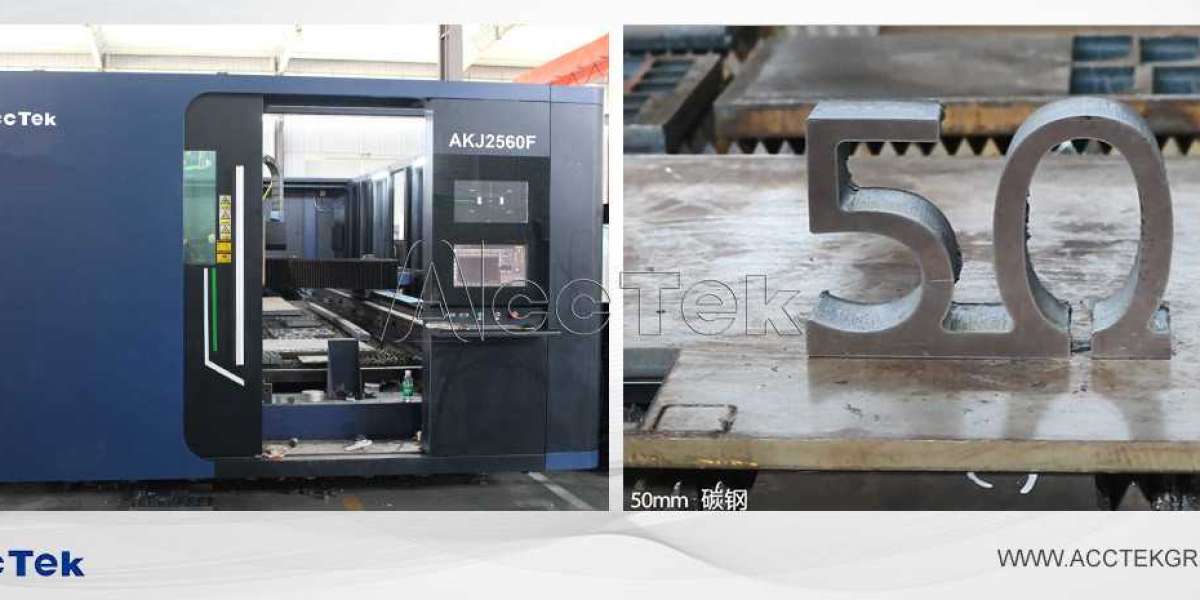
Fiber laser can well cut stainless steel, titanium, cobalt chromium, nickel titanium alloy and other thick metals with a cutting thickness of 0.5~3mm.
Therefore, fiber laser is an ideal choice for large surgical drills with cutting saws, blades and couplings. However, as optical fiber laser cutting is a hot processing process, burrs, slag inclusions and heat affected zones usually appear after cutting parts. Therefore, only after electropolishing and other post-treatment cleaning technologies are used for rolling and deburring, can the processed products be polished and cleaned before use.
In the manufacture of medical devices, laser has become laser marking and welding. It is widely used in cutting and other technological processes. It is very important to select the laser suitable for each processing process to achieve the desired processing effect and stable repeatability. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the process foundation provides new opportunities to promote innovation in the field of medical devices.