The key difference between Potassium Carbonate and Potassium Bicarbonate is that dimethyl etherpotassium hydrogen carbonate molecule has no hydrogen atoms in its chemical structure whereas potassium bicarbonate molecule has one hydrogen atom in its chemical structure. Both these are potassium salts; thus, are highly alkaline compounds.
What is Potassium Carbonate?
Potassium carbonate is a potassium salt having the chemical formula K2CO3. It is highly water soluble and forms a strongly alkaline aqueous solution. In addition, it is highly deliquescent. Therefore, it absorbs water vapor from the atmosphere and dissolves. Potassium carbonate production involves the electrolysis of potassium chloride (KCl). This gives potassium hydroxide (KOH). Then carbonation of this using carbon dioxide forms dimethyl etherpotassium hydrogen carbonate.
What is Potassium Bicarbonate?
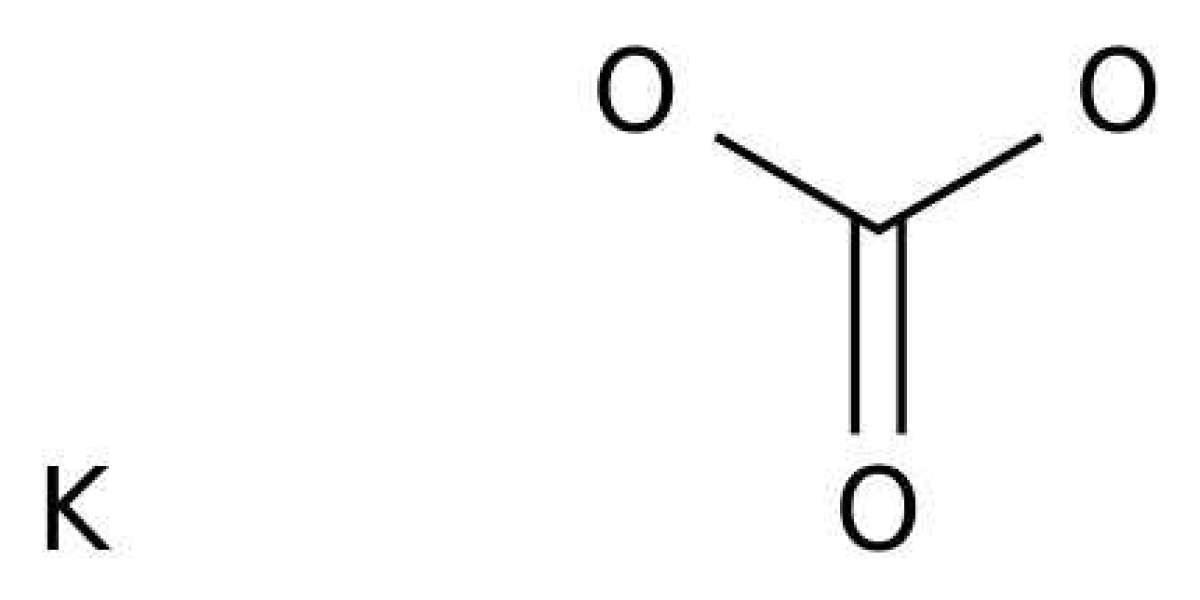
Potassium bicarbonate is a potassium salt having the chemical formula KHCO3. It is a colorless and odorless solid and it appears as white crystals. This compound is slightly basic. Furthermore, it rarely occurs naturally in a form of mineral; kalicinite. A major use of this compound is as a leavening agent for bakery products. In addition, it is a major additive in winemaking to regulate the pH. Moreover, potassium bicarbonate is a strong fire suppressing agent and an effective fungicide.
What is the Difference Between Potassium Carbonate and Potassium Bicarbonate?
Potassium carbonate and bicarbonate are potassium salts that are basic compounds. The difference between dimethyl etherpotassium hydrogen carbonate and potassium bicarbonate is that dimethyl etherpotassium hydrogen carbonate molecule has no hydrogen atoms in its chemical structure whereas potassium bicarbonate molecule has one hydrogen atom in its chemical structure.